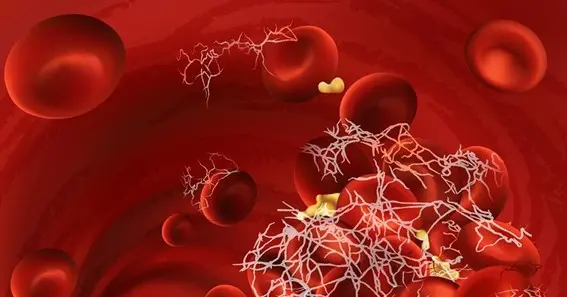
Before knowing the fibrin monomer, you should know exactly what fibrin is. Well, fibrin is nothing but the insoluble protein that is produced in response to bleeding and is the major component of the blood clot. If you get a cut and you see the blood come out, but after a few seconds or within a minute the blood flow automatically stops. Why does this happen? It is because the fibrin protein makes a mesh-like structure that clots the blood. It is a tough protein substance that is arranged in a long fibrous chain. Fibrin is formed from fibrinogen, which is a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma. Let me tell you more about the fibrin monomer.
What Is Fibrin Monomer?
Fibrin monomer is the monomer of fibrin which is formed by the cleavage of fibrinogen by thrombin. When your body tissue gets damaged and results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme. Fibrin molecules then combine to form long fibrin threads that entangle platelets, building up a spongy mass that gradually hardens and contracts to form the blood clot. This hardening process is stabilized by a substance known as fibrin-stabilizing, or factor XIII.
What is fibrin monomer test? Well, it is an assay used to monitor the proteolytic cleavage of fibrinogen by thrombin and the resulting generation of soluble fibrin monomers. So, fibrin monomers are increased in which of the following conditions? They increase the condition of primary fibrinolysis.
Now, you have understood the soluble fibrin monomer test positive meaning. So, let us know the properties of the fibrin monomer.
Also Read : What Is PVC Monomer?
Properties Of Fibrin Monomer
The fibrin monomer properties are,
- Fibrin is a viscoelastic compound, which means that it has both viscosity and elasticity properties.
- The elasticity is characterized by reversible mechanical deformation, while viscosity is characterized by irreversible deformation induced by force.
Also Read : What Is Methyl Methacrylate Monomer?
Fibrin Structure And Function
Here is the structure as well as the function one after another, of the fibrin.
Click here – What Is PVC Monomer?
Fibrin Structure
The fibrin molecule has an elongated shape of 45 nm in length and approximately 2 to 5 nm in diameter. Plasmin cleaves fibrinogen into a number of core fragments, namely fragment E comprising the central part of the molecule and two identical segments of D originating from the lateral parts of fibrinogen.
The fibrinogen molecule has two distal globular D regions and one central globular E region each containing a part of alpha-helical coiled coils.
Fibrin Function
Fibrin is also called Factor, and its main function is to clot the blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with platelets, forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site.
They are essential for blood clot contraction, that is, spontaneous shrinkage of the clot, which plays a role in hemostasis, wound healing, and restoring the flow of the blood past obstructive thrombi.
Facts About Fibrin
Here are some facts about fibrin are,
- Fibrin is an insoluble protein that is produced in response to bleeding and is the major component of the blood clot.
- Fibrin is formed from fibrinogen, a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma.
- Fibrin is an ough protein substance that is arranged in long fibrous fibers.
So,Is fibrinogen is converted to fibrin monomers by Quizlet? Yes, thrombin helps convert fibrinogen to fibrin.
Follow Monomerof to know more about various monomers.
FAQ
What Is Fibrin Monomer Test?
Fibrin monomer tests are assays used to monitor the proteolytic cleavage of fibrinogen by thrombin and the resulting generation of soluble fibrin monomers. Fibrin monomer assays give direct evidence of thrombin activity on fibrinogen.
How Do Fibrin Monomers Are Produced?
Fibrin monomers are intermediate products formed during the proteolysis of fibrinogen by thrombin. During the intravascular coagulation, low levels of thrombin are available in the blood, but the fibrin monomers formed are not in sufficient quantities to aggregate and form a clot.
What Is Fibrin Made Of?
Fibrin is a tough protein substance that is arranged in long fibrous chains; it is formed from fibrinogen, a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma. When tissue damage results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme.
What Stimulates The Formation Of Fibrin?
Blood-clotting proteins generate thrombin, an enzyme that converts fibrinogen to fibrin, and a reaction that leads to the formation of a fibrin clot tissues outside the vessel stimulates thrombin production by the activation of the clotting system.
What Are Fibrin Molecules?
Fibrin is a tough protein substance that is arranged in long fibrous chains; it is formed from fibrinogen, a soluble protein that is produced by the liver and found in blood plasma. When tissue damage results in bleeding, fibrinogen is converted at the wound into fibrin by the action of thrombin, a clotting enzyme.
Click here – What Is Methyl Methacrylate Monomer?
What Is Soluble Fibrin Monomer?
Soluble fibrin monomer complexes (SFMCs) are precursors of fibrin polymer formation. Laboratory tests can be used to detect SFMCs in plasma.
What Is A Fibrin Polymer?
Fibrin polymer is an end product of the enzymatic cascade of blood clotting. In vivo formation of the polymeric fibrin network, along with platelet adhesion and aggregation, are the key events in salutary stopping of bleeding at the site of injury (hemostasis) as well as in pathological vascular occlusion (thrombosis).
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned about a very important component which is the fibrin monomer. Do you know? Certain rare hereditary disorders may cause malfunction of this stage of the blood-clotting mechanism. A few individuals have a hereditary deficiency of fibrinogen or produce abnormal fibrinogen. Upon injury, to these persons, fibrin cannot form in sufficient quantity to enable a proper clot to form. Another rare hereditary disease involved a lack of factor XIII, resulting in a condition in which bleeding is difficult to stop. So, this was all about the fibrin monomer.
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit truelynutrition
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit OfAdvantages
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit Richestic
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit CountSpeed
To Know Some Great Stuff Do Visit squareroott
What is a fibrin monomer
What is a fibrin polymer